- Home/
-
About Us/
-
Doctors and Services/
-
Ward and Services/
-
News/
Recently, a patient with stubborn hyperlipidemia, Mr. Wu (a pseudonym), aged 43, visited Foresea YiHe International Medical Center. The pre-treatment lab results showed alarmingly high triglycerides and total cholesterol levels, reaching 35.03 mmol/L and 7.69 mmol/L, respectively.
(Normal reference range: 0-2.3 mmol/L, 0-5.2 mmol/L).
After understanding the principles, efficacy, and safety of therapeutic lipid apheresis, the international medical center performed the treatment on the patient. During the procedure, the separated plasma appeared milky due to excessive lipids (lipemic plasma). Following lipid apheresis, repeat testing showed a significant reduction in triglycerides and total cholesterol to 6.47 mmol/L and 2.52 mmol/L, respectively, demonstrating notable improvement.
(Normal reference range: 0-2.3 mmol/L, 0-5.2 mmol/L).
How dangerous is hyperlipidemia?
What is lipid apheresis technology? Which diseases can it treat?
What are the advantages of blood lipid purification technology? What results can be expected?
In this issue, we will focus on the difficult-to-manage high cholesterol and the advanced lipid apheresis technology, answering your questions in detail.
Foresea Yihe International Medical Center has officially introduced the Lipid Apheresis Therapy Program. Tailored to each patient’s lipid profile and metabolic risk factors, we provide a personalized treatment plan that covers Baseline lipid assessment, Intra-procedural lipid monitoring during treatment, and Post-procedural management. This program offers a safe and effective new option for Treating dyslipidemia.
Project Package
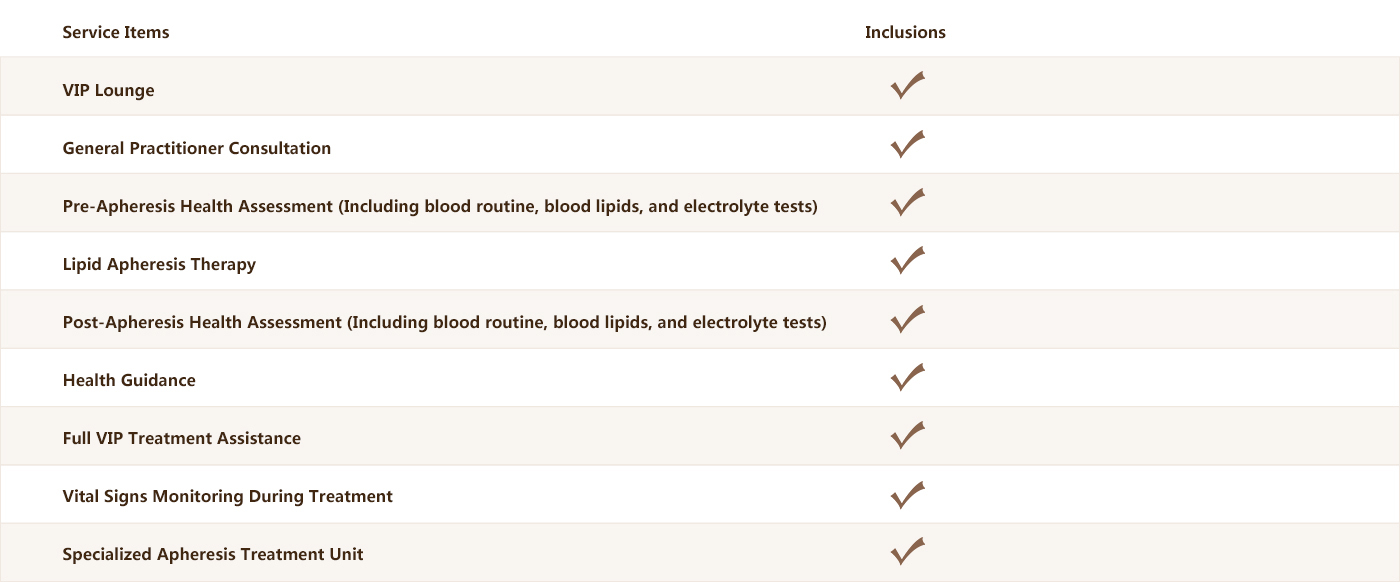
If you are facing challenges in managing your blood lipid levels, you can contact Foresea YiHe International Medical Center at (020-32996999) for consultation. We will arrange an expert appointment for you as soon as possible and provide a face-to-face consultation, tailoring a Lipid Apheresis Treatment plan based on your individual condition.
Hyperlipidemia, a type of dyslipidemia, typically refers to elevated levels of triglycerides (TG) and/or total cholesterol (TC) levels in the blood plasma, increased low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and decreased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C). The main dangers include:
Chronic hyperlipidemia can lead to lipid accumulation in arterial walls, contributing to the development of atherosclerosis. This can cause arterial stenosis and occlusion, potentially leading to coronary artery disease (CAD), acute myocardial infarction (AMI), hypertension, and ischemic stroke.
Peripheral artery disease (PAD), particularly affecting the lower limbs, can cause arterial stenosis or occlusion, leading to claudication and ischemic pain. In severe cases, critical limb ischemia (CLI) may develop, leading to tissue necrosis and potential limb amputation.
Severe hypertriglyceridemia can trigger acute pancreatitis. can cause acute pancreatitis. The mortality rate for severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) ranges from 30% to 50%.
Furthermore, hyperlipidemia is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, including coronary artery disease (CAD), ischemic stroke, myocardial infarction (MI), and sudden cardiac death (SCD).
Blood lipid purification is a treatment method that utilizes extracorporeal blood purification therapy and plasma exchange and selective lipid filtration technology.
It works by selectively removes excess cholesterol, triglycerides, and atherogenic lipoproteins from the blood, aiming to correct dyslipidemia, reduce blood viscosity, improve blood circulation, and slow the progression of atherosclerosis. This treatment offers an effective approach to managing hyperlipidemia, especially for patients who do not respond well to medication.
01.Vascular Access: A venous catheter is placed in both arms—one side is used to draw blood, and the other side is used to reinfuse the blood.
02.Plasma Separation: The drawn blood passes through the first filter, known as the Plasma separator, which separates the cellular components (such as red blood cells, white blood cells, etc.) from the plasma. The plasma then enters the Secondary filtration system, where targeted lipid components are selectively removed and purified.
03.Reinfusion: The Treated plasma is mixed with the cellular components separated in the primary membrane and is then returned to the patient's circulation.
Severe refractory hyperlipidemia
Cardiovascular disease (CVD), Cerebrovascular disease (CeVD), Chronic kidney disease (CKD), Hypertriglyceridemia-induced acute pancreatitis (HTG-AP), Metabolic syndrome (MetS) with dyslipidemia, Acute arterial occlusion due to atherosclerosis, Retinal artery occlusion (RAO) and Sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL)
01.Short time: Each session typically lasts 2-3 hours.
02.Minimally invasive: Generally, complex vascular access is not required, just two Peripheral venous access.
03.Selective filtration: Only cholesterol, triglycerides, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol are filtered out, without losing beneficial components of the body.
04.High efficacy: One treatment can reduce total cholesterol, triglycerides, and Atherogenic lipoproteins by up to 90%.
05.Low risk: The procedure operates in a closed extracorporeal circulation system, with the blood not being exposed to external factors. It selectively removes Pathogenic lipoproteins, and While reinfusing the patient’s own plasma, reducing the risk of infection or transmission of diseases.
01.Correcting dyslipidemia:Significant reduction in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), Lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)], and triglycerides, with preservation of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C).
02.Enhancing hemorheology:Reduces oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL), Reduces levels of P-selectin, soluble adhesion molecules, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), and fibrinogen.
03.Enhancing endothelial function:3.Reduction in total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)], Enhancing endothelial function and vascular responsiveness.
References:
Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Dyslipidemia in Chinese Adults (2016 Revised Edition)
Chinese Guidelines for Lipid Management (2023)
Expert Consensus on Non-Biological Artificial Liver Devices and Technology